Thyroid
Thyroid Tumour
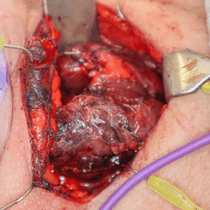
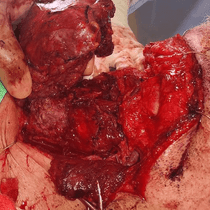
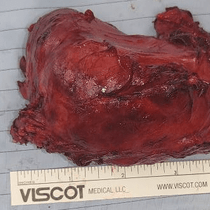
A thyroid tumour refers to an abnormal growth or mass that develops within the thyroid gland. These tumors can be benign or malignant (cancerous). They arise from abnormal growths of thyroid follicle cells and can manifest as nodules within the thyroid gland. Adenomas are the most common type of benign thyroid tumour and can be further classified into benign adenomas and follicular adenomas. Fluid-filled sacs called cysts may appear within the thyroid gland; they are often benign and usually asymptomatic unless they grow large enough to cause symptoms.
Common symptoms can include a palpable lump or swelling in the neck, changes in voice quality, difficulty swallowing, and in some cases, symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism depending on the type of tumour and its effect on thyroid hormone production.
Surgery is typically recommended for definitive diagnosis, with molecular testing sometimes used on repeat FNAs to assess malignancy risk. Treatment often involves removing the affected thyroid lobe, which is then examined to determine if the tumour is cancerous. In cases where malignancy is confirmed, a lobectomy may be sufficient; however, more aggressive forms may necessitate a complete thyroidectomy to prevent recurrence.