Paediatric ENT Conditions
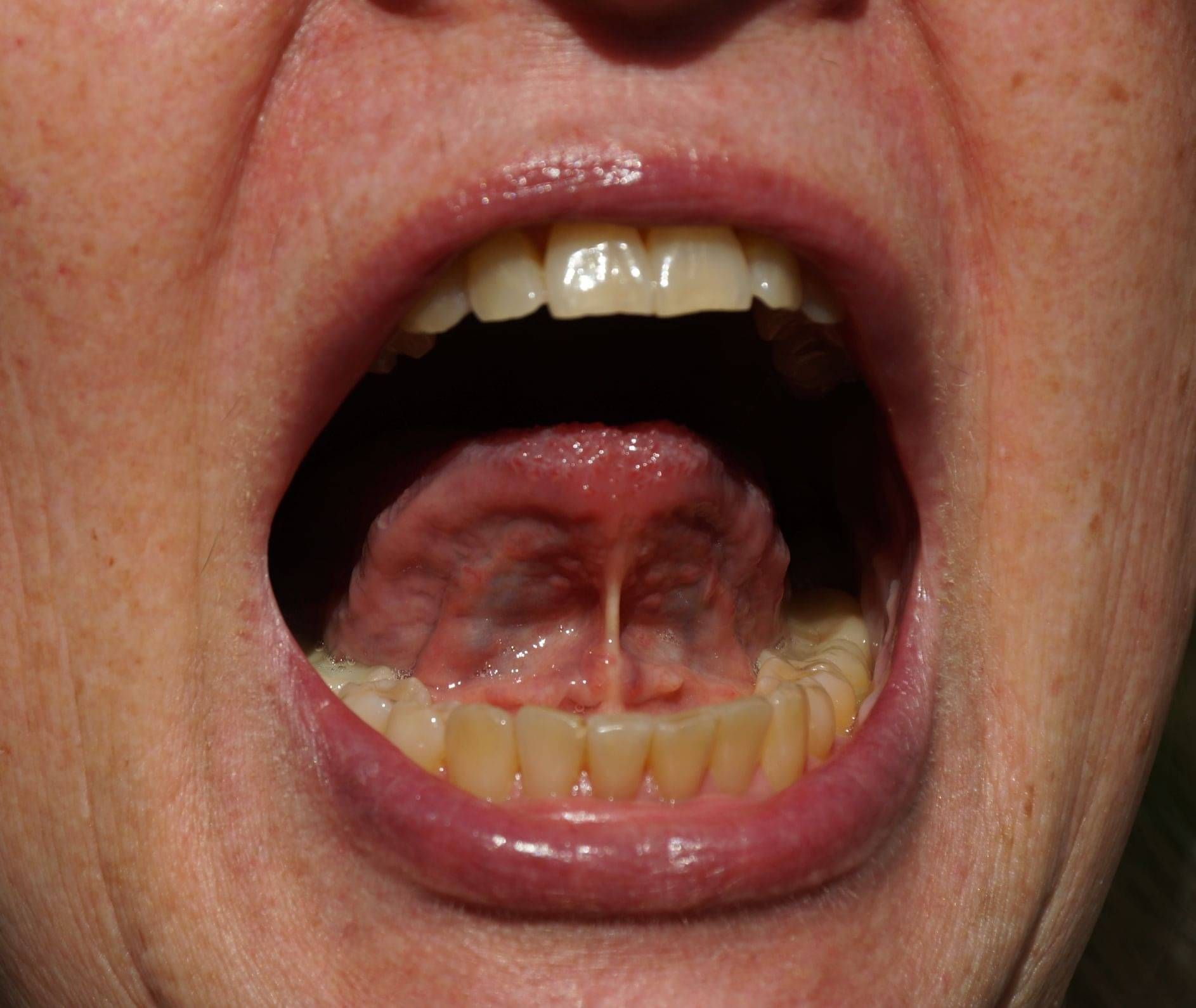
Tongue Tie
Tongue tie, or ankyloglossia, is a condition where the thin piece of tissue (lingual frenulum) that connects the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth is shorter, thicker, or tighter than usual. This can restrict the movement of the tongue and may affect various functions such as feeding, speech, and oral hygiene. While often asymptomatic, it can hinder newborns' tongue movement, causing breastfeeding difficulties. In older children and adults, tongue tie can contribute to speech difficulties, particularly with certain sounds like "t," "d," "l," and "r." There may also be some difficulty reaching and cleaning the back teeth or clearing food from the mouth.
Concerns about appearance or potential interference with activities like licking lips or kissing often prompt parents to seek treatment. The condition typically improves with age, and there is no proven link between tongue tie and speech or language issues. Treatment, when necessary, usually involves a straightforward procedure to release the frenulum.
Once a physical exam is done, the child may undergo a quick and simple frenotomy procedure. The surgeon clips or snips the frenulum to release the tongue tie. This is often done in infants using local anaesthesia. In more severe cases or when the frenulum is thicker, a more complex surgical procedure called frenuloplasty may be required to release the tongue tie.