Surgeries for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA)
SMILE (Submucosal Minimally Invasive Lingual Excision)
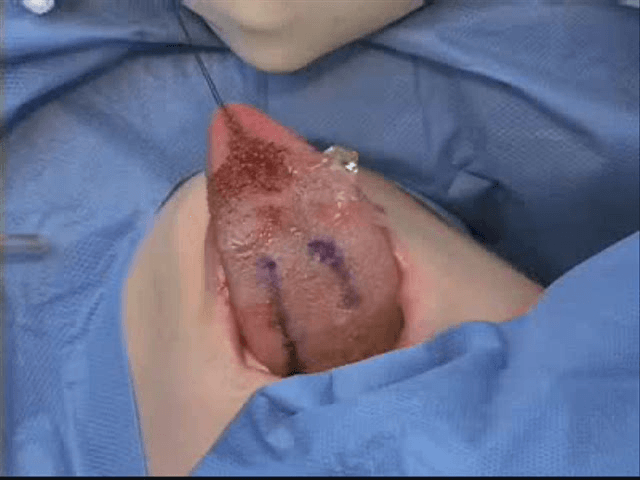
SMILE is a surgical procedure designed to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) by addressing the anatomical factors contributing to airway obstruction at the base of the tongue. It reduces the volume of obstructive tissue in the tongue base, thereby improving airway patency and reducing symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea such as snoring and disrupted breathing during sleep.
SMILE involves making small incisions in the tongue's mucosal layer to access and remove excess tissue from the base of the tongue, specifically targeting the lingual tonsils or other obstructive tissues. The procedure is performed through the mouth, avoiding external incisions, and is guided by endoscopic visualization to precisely identify and target the lingual tonsils or hypertrophic tissues causing obstruction.
SMILE has shown effectiveness in improving airway dynamics and reducing symptoms of sleep apnoea in selected patients. Compared to more invasive surgeries like traditional base of tongue resection, SMILE typically results in reduced post-operative pain, faster recovery times, and lower risk of complications. Surgeons may use specialised tools such as lasers or coblation devices to perform tissue removal with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.