General ENT Conditions
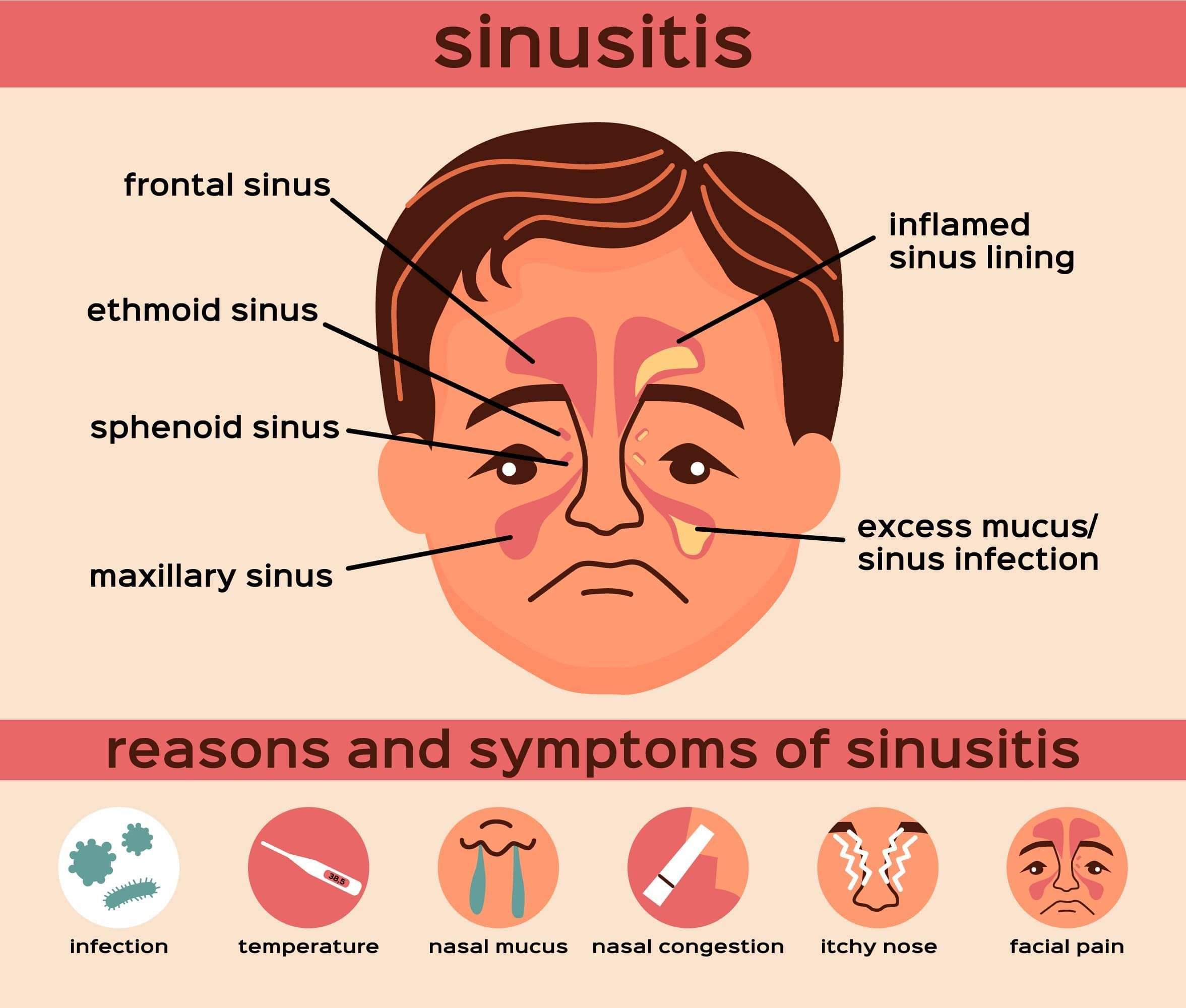
Sinusitis
Sinusitis specifically refers to inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled cavities around the nasal passages. Sinusitis typically occurs when the sinuses become blocked and filled with fluid due to infection (bacterial, viral, or fungal) or other causes such as allergies or structural abnormalities (like a deviated septum). Symptoms of sinusitis include facial pain or pressure, nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, cough, and sometimes fever.
Sinusitis can be acute (lasting less than 4 weeks), subacute (lasting 4 to 12 weeks), chronic (lasting more than 12 weeks), or recurrent (multiple acute episodes within a year). When sinusitis coexists with rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal passages), it is referred to as rhinosinusitis.