Salivary Gland Disorders
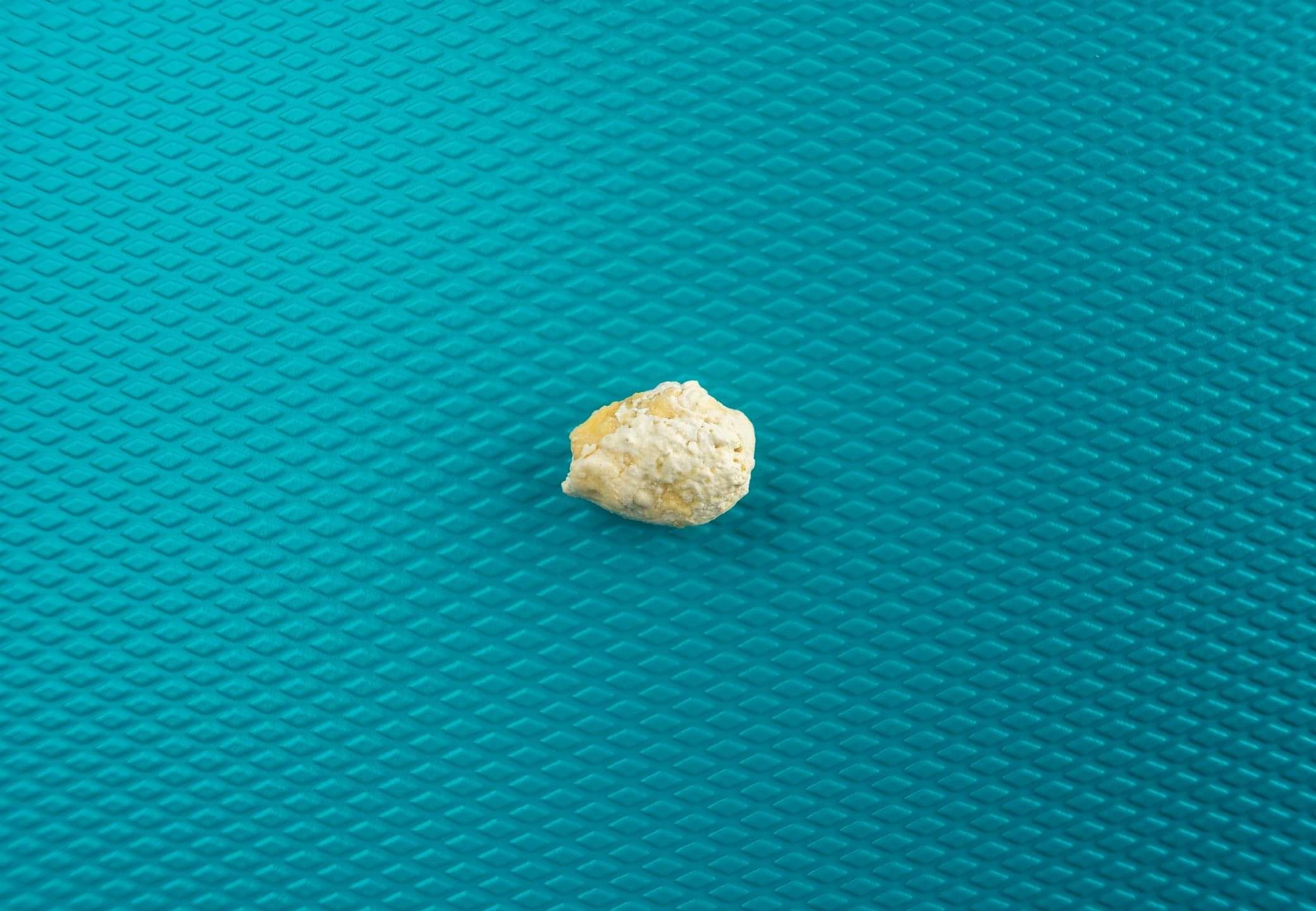
Sialolithiasis (Salivary Stones)
When salivary flow of gland slows down then it gets reposited to form stone which will cause swelling and pain in the gland. Sialolithiasis can affect any of your salivary glands and symptoms may occur on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral).
These symptoms may include: swelling of the gland, difficulty swallowing, trouble opening your mouth, dry mouth (xerostomia), strange taste, a painful lump under your tongue, facial pain or swelling. Any condition that causes thickening of your saliva can result in sialolithiasis including dehydration, smoking and certain autoimmune diseases such as lupus and Sjögren’s syndrome; certain medications such as diuretics; trauma to your salivary glands; or radiation therapy to your mouth.
In some cases, people with sialolithiasis do not develop any symptoms at all and some may develop salivary gland stones even when there is no apparent cause.
Symptoms should be evaluated by an Ear, Nose and Throat surgeon who will conduct a physical examination to reveal lumps or other abnormalities. Furthermore, imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT and/or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis or to locate any of the salivary gland stones.
Sialolithiasis treatment depends on the size and location of the stone, and may include home remedies, antibiotics, in-office stone removal or in some cases, surgery or sialendoscopy.