Salivary Problems & Sialendoscopy
Salivary Glands
The function of the salivary glands in the head and neck is to secrete saliva aiding in the functions associated with the mouth, such as chewing, swallowing, digesting and speaking. Among the major pairs of salivary glands, parotid is largest, lying below and just in front of the ears. A tube called the Stensen’s duct drains saliva from the glands into the mouth. Although 5 cm long, its diameter is only 1-2 mm and opens inside the cheek opposite the upper molars.
Lying deep in the horizontal part of the lower jaw are the submandibular glands; their ducts are the narrowest of all the salivary glands; they enter the mouth from two sides under the tongue at the front of the mouth.
Additionally, there are the sublingual glands and hundreds of minor salivary glands all along the lining of the mouth and throat with most on the lips and palate.
Not only do these glands secrete saliva when food enters the mouth, but the mere thought or smell of food can stimulate its secretion. Although mostly made of water, saliva comprises of proteins and minerals that help digest food. It also aids in maintaining healthy teeth and mouth. Most people make about 1 litre of saliva per day.
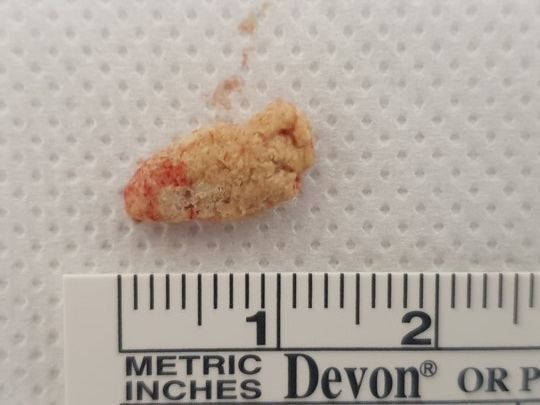
Salivary Gland Disorders
Each of these glands is prone to major problems including, but not limited to:
Salivary Gland Treatments & Operations
A Sialendoscopist evaluates your salivary symptoms clinically and also accesses indications radiologically using Ultrasound / CT Scan / MRI Sialogram to make a diagnosis. There are a few approaches that may follow:
Referral Pathway
We provide online consultations within two weeks of referral for out-of-town residents.
Ultrasound/CT/MRI can be undertaken in the patients’ city.
Referral → In person / Online consultation / Radiological Investigations in patient’s city →
Treatment Planning through Online Consult → Fly in - Sialendoscopy – One Night Stay – Fly out
Private and outsourced referrals can be sent to: admin@entcentral.co.nz















