Salivary Gland Disorders
Sialadenitis
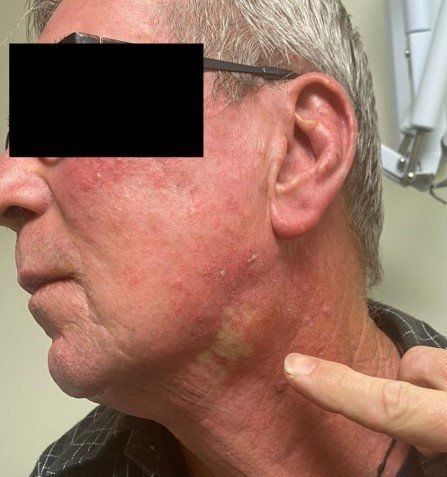
Salivary glands can become enlarged repeatedly due to some obstruction in the salivary duct system caused by stone or stricture (narrowing of the duct). This distinct type of enlargement associated with eating and drinking is most common in the parotid and submandibular glands. Sometimes harmful virus or bacteria are usually to blame. Mostly, the gland on the whole is affected, although focal/partial swelling can also occur. One may also note a sudden gush of salty fluid into the mouth.
The inflammation can be painful lasting 20 minutes for some people or even up to a week or more in others. The frequency of episodes of swelling varies greatly from 2-3 times per day to once every ten years or so. Those affected may experience symptoms ranging from pain in the mouth and jaw region, tenderness and redness to gradual localised swelling of the affected area. Frequent episodes of tender swelling can lead to chronic sialadenitis.
Salivary stone or the narrowing of the salivary duct may be detected using an ultrasound scan or CT scan. Sialendoscopy is often undertaken to help treat chronic sialadenitis.