Approaches & Techniques
Nasoseptal Reconstruction With Septoplasty
A nasoseptal reconstruction, often referred to as nasoseptal reconstruction surgery or septal reconstruction, is a specialised surgical procedure performed to correct and reconstruct the nasal septum. The nasal septum is the thin wall of cartilage and bone that divides the nasal cavity into two sides. It plays a crucial role in nasal structure, support, and airflow.
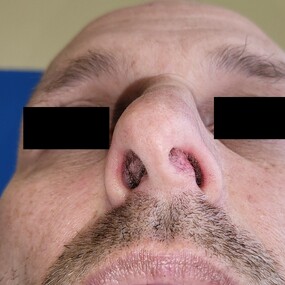
A Deviated Septum is a significant shift in the nasal septum which can obstruct sinus drainage and airflow, contributing to sinus infections and congestion and sometimes nosebleeds, and snoring. A septoplasty is done to correct this issue. Sometimes the septum is significantly deviated (crooked) by birth of following nasal trauma or injury leading to severe septal damage or displacement. This may cause extreme nasal deformity and accompanies extreme nasal obstruction. A nasoseptal reconstruction is then performed along with septoplasty.
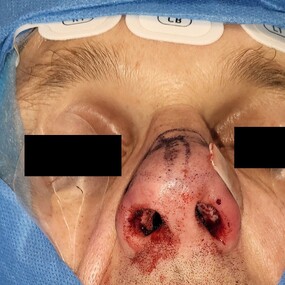
Although an endonasal incision is made to access the nasal septum, an open approach may sometimes be required for more complex cases. The surgeon may straighten, reshape, or remove damaged portions of the septum. Cadaveric graft and fascia and other cartilage grafts harvested from the nasal septum itself or other areas of the body (e.g. ear or rib) may be used to rebuild and reinforce the septal structure. Additional techniques such as septal splints, nasal packing, or sutures may be used to support the reconstructed septum and promote proper healing. Once the reconstruction is completed, incisions are closed with dissolvable sutures, and nasal packing or splints may be placed temporarily.
Nasoseptal reconstruction which includes septoplasty, is generally done as a combined procedure with sinus surgery, turbinoplasty or a nose job (septorhinoplasty). Hence, surgery duration can vary between 45 mins and 2 hours.
Benefits
Improved airflow, enhancing breathing and reducing symptoms of nasal congestion.
Better looking appearance of nose, particularly in cases of visible asymmetry.
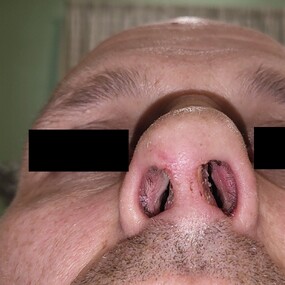
Long-term structural stability and support for nasal framework.
Improved quality of life due to satisfactory nasal function and appearance.