Thyroid
Hyperthyroidism & Hypothyroidism
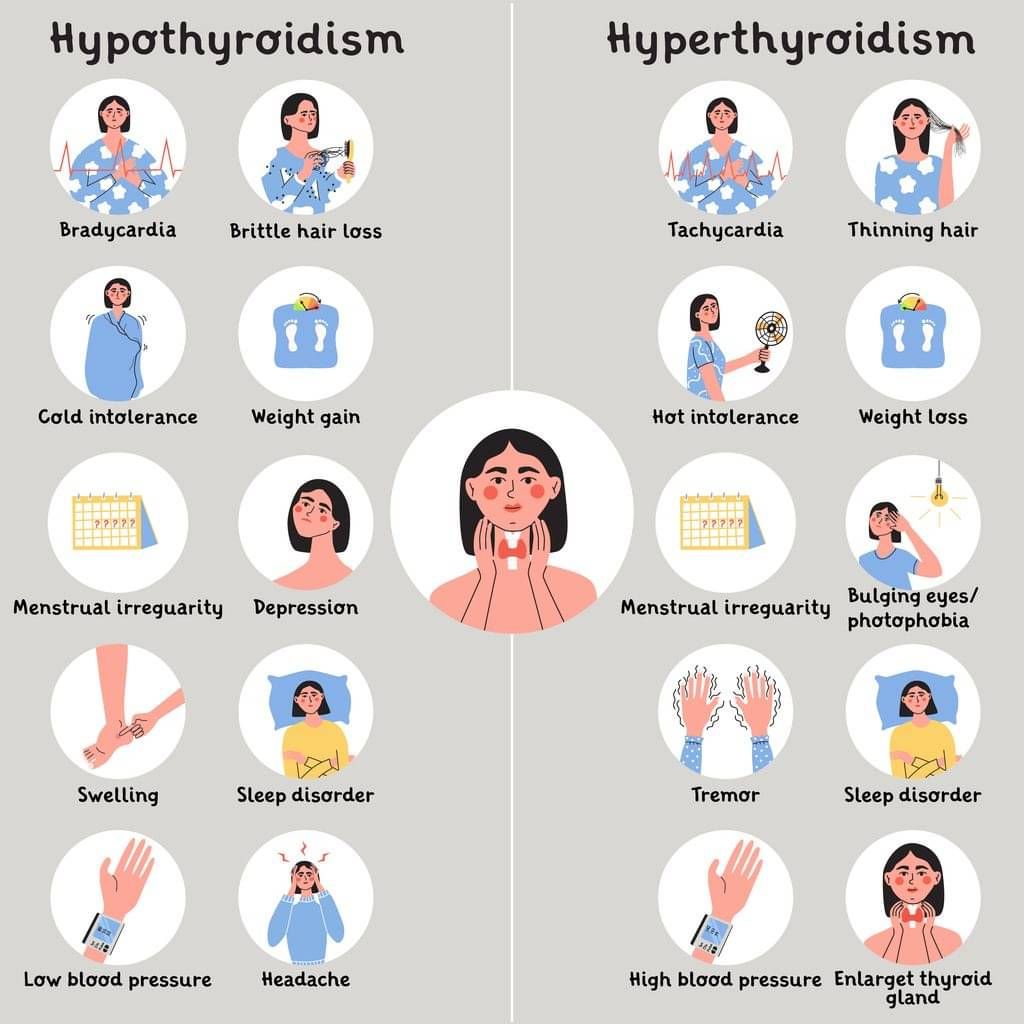
Characterised by excessive thyroxine secretion, hyperthyroidism results in heightened metabolic activity, leading to symptoms such as tremors, heat intolerance, irritability, increased energy, sleep disturbances, weight loss and often, protruding eyes. Conversely, hypothyroidism, caused by insufficient thyroxine production, lowers metabolic rate, causing symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, swelling, and slowed speech and thought.
Diagnosis of thyroid disorders involves a simple blood test to measure thyroxine levels. Treatment for hyperthyroidism includes medications to inhibit hormone release and effects; radioactive iodine therapy to destroy the thyroid gland by uptake of iodine; or surgical removal of the thyroid. Hypothyroidism is effectively managed with daily thyroxine supplementation.