Hyperparathyroidism
Symptoms
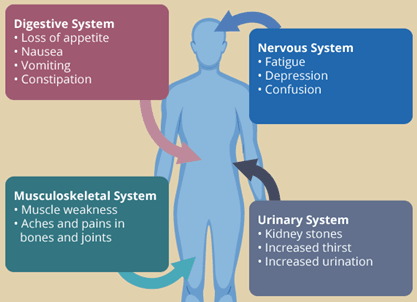
Many individuals with primary hyperparathyroidism are asymptomatic and are diagnosed incidentally during routine blood tests that reveal elevated levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcaemia). Hypercalcaemia can lead to the formation of stomach ulcers and contribute to abdominal pain and discomfort. High calcium levels can also lead to dehydration, exacerbate existing high blood pressure, and contribute to a feeling of overall tiredness.
Chronic overproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH) can lead to bone mineral loss, resulting in osteoporosis and an increased risk of bone fractures. In more severe cases, elevated calcium levels can affect neurological function causing symptoms such as mental confusion or cognitive impairment. Patients may also experience symptoms like kidney stones, constipation, fatigue, weakness and even depression.
Several underlying abnormalities can trigger primary hyperparathyroidism with symptoms being nonspecific and possibly overlapping with various other medical conditions. This can make diagnosis challenging. It is essential for individuals experiencing unexplained symptoms, especially those at higher risk (such as older women), to undergo thorough evaluation, including blood tests, to assess calcium levels and PTH.