Hyperparathyroidism
Diagnosis & Treatment
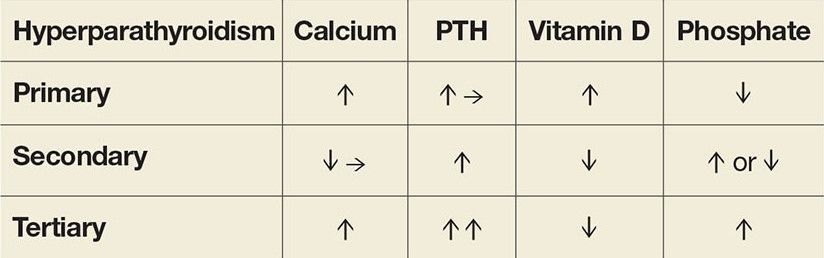
Diagnosis begins with blood tests that reveal elevated calcium and PTH levels. Other blood tests will reveal kidney function, and vitamin D & alkaline phosphatase levels. Urine tests will show 24-hour urine calcium level and the calcium/creatinine ratio. Overall, these tests help distinguish primary hyperparathyroidism pathology from others that may show high calcium level.
Patients are then usually recommended to have an ultrasound, a Sestamibi scan and/or a 4DCT scan to identify the specific parathyroid gland that is over-producing the parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid surgery (parathyroidectomy) is the go-to treatment for most patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, during which a rapid parathyroid hormone assay is also done.
Those with secondary hyperparathyroidism resulting from a vitamin D deficiency may be asked to take vitamin D supplements.