Nose Pathology
Epistaxis (Nose Bleeds)
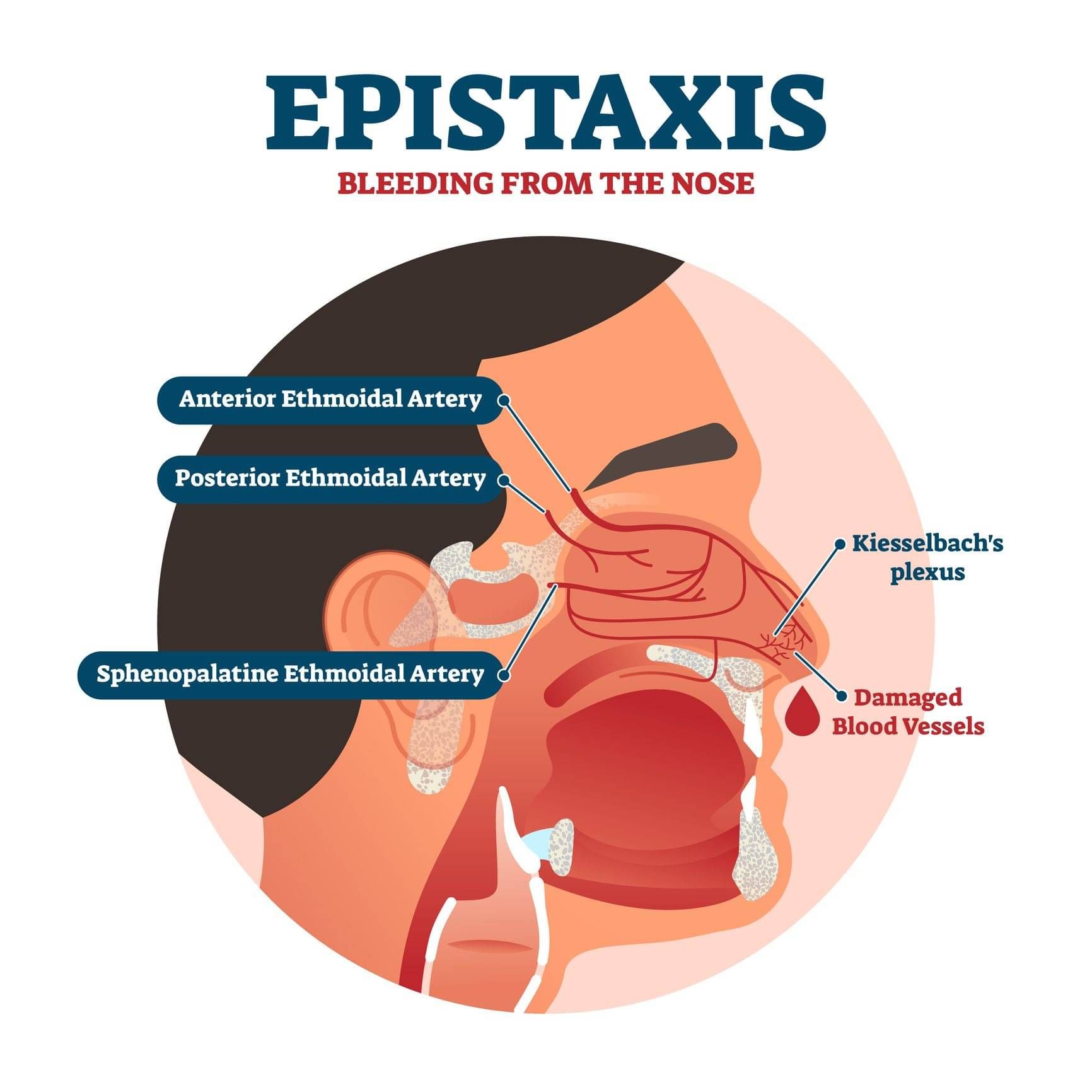
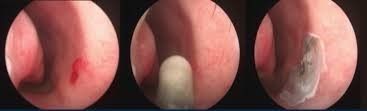
Epistaxis, commonly known as a nosebleed, occurs when blood vessels within the nose rupture and bleed. They are among the most frequently encountered conditions in ear, nose, and throat medicine. Nosebleeds are particularly common in children and often respond well to treatment with silver nitrate, a chemical applied to the problematic blood vessel after numbing the nose with an anesthetic spray. This procedure is painless for the child and typically resolves the issue with just one treatment.
While often not serious, nosebleeds can be alarming and occasionally require medical attention especially when they are persistent or recurring. Adults may require more extensive investigation to determine the source of nosebleeds, which can originate from deeper locations or within the sinus cavities.
Causes of nosebleeds can range from dry air, nose picking and nasal infections to trauma (injuries and accidents), medical conditions (high blood pressure, clotting disorder etc.) and medications like blood thinners (anticoagulants) or nasal sprays. For this reason, a CT scan may be necessary to identify the cause.
While self-care measures may work in some cases, medical interventions like cauterisation and nasal surgery may be required to put an end to the bleeding. Treatment for adults generally mirrors that for children, though occasionally more serious underlying conditions may be discovered.