Coblation Assisted Surgeries
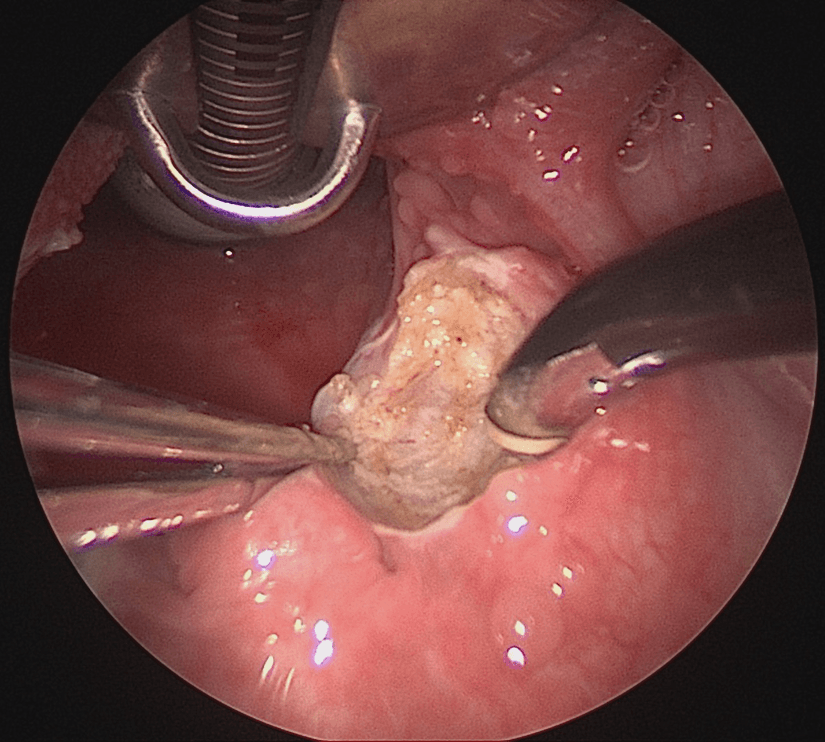
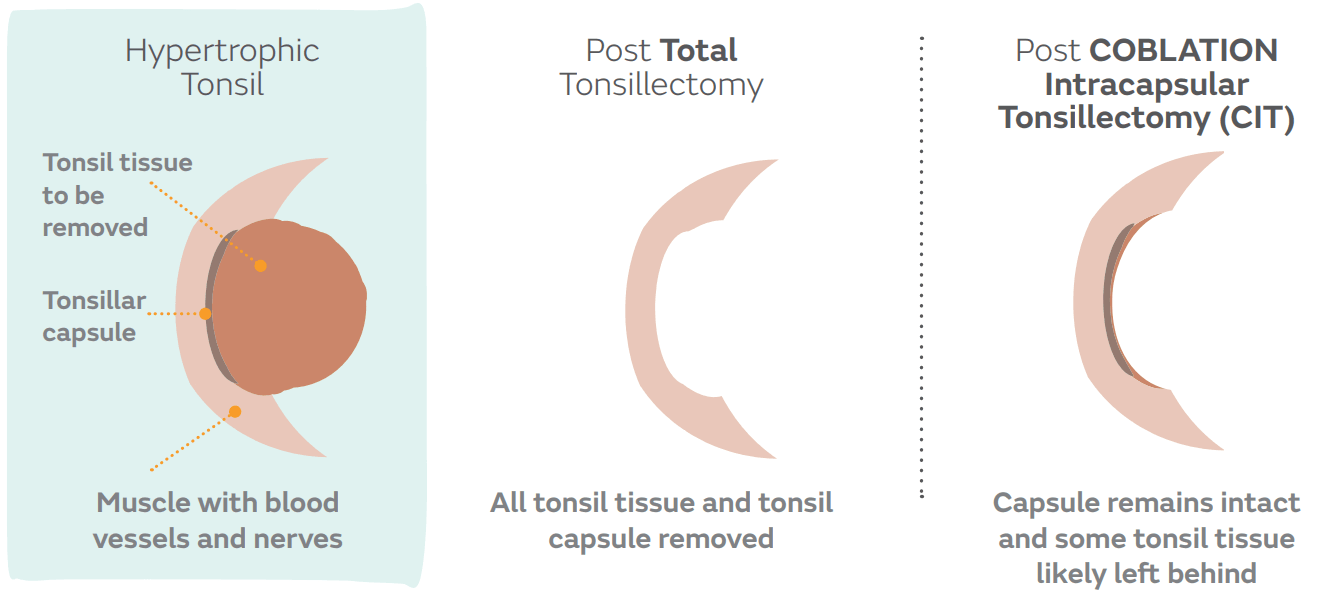
Coblation Tonsillectomy
Studies have shown that following surgery, patients receiving coblation tonsillectomy reported less severe pain over 10 days compared to those treated with electrocautery and Harmonic Scalpel. Secondly, coblation intracapsular tonsillectomy (CIT) showed excellent results for both obstructive and infective symptoms, leading to excellent symptom control, comparing favourably with existing literature for extracapsular tonsillectomy. There was a low rate of complications and rapid patient recovery. Lastly, children receiving CIT for sleep apnoea or sleep-disordered breathing had better postoperative recovery versus those receiving coblation submucosal tonsillectomy, most pronounced at a delayed time point (5 or 6 days), rather than early (1 or 2 days).