Coblation Procedures
Coblation Tonsillectomy
COBLATION Technology (clicking this connects to coblation interactive pdf / opens on separate tab: https://mytonsils.com/) is a relatively low temperature surgical method to precisely remove tissue. COBLATION is an acronym for controlled ablation (or cold ablation) which is the process of size reduction using relative heat. Radiofrequency energy is used to create a plasma field of ionised particles within a conductive medium (such as saline solution). This plasma field gently and precisely dissolves tissue at low temperatures (typically below 70°C), minimising damage to surrounding healthy tissue resulting in less pain after surgery. Longstanding methods like electrocautery, use high temperatures to cut and cauterize tissue, often leading to painful damage of nearby tissue. In comparison, thermal penetration of coblation-based devices is minimal with dissolution of target tissue taking place in a precise, gentle and controlled manner with no burning or charring of the nearby tissue. Coblation technology has been gaining ground in surgical applications in various branches including ENT. Some of them are: Turbinate Channeling and Sinus Surgery; and treatment of laryngeal lesions caused by HPV (no plume), tumours and stenosis, besides tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (low blood loss).
COBLATION technology used in a COBLATION Tonsillectomy (clicking this opens on separate tab: https://mytonsils.com/) or adenoidectomy allows for the gentle removal of the tonsils (or adenoids) during a scheduled tonsillectomy procedure. Surgeons use a coblation wand to remove the tonsils. There are two approaches to COBLATION tonsillectomy: intracapsular tonsillectomy (CIT) or extracapsular tonsillectomy, also known as total tonsillectomy. Both of these techniques have been proven favourable for both patients and physicians.
CIT utilizes Coblation technology to target and remove only the diseased tissue within the tonsil while leaving the outer shell (capsule) intact. This approach aims to reduce post-operative pain and speed up recovery compared to traditional tonsillectomy techniques, making it a preferred option for some patients, particularly children and adults with recurrent tonsillitis or sleep-disordered breathing.
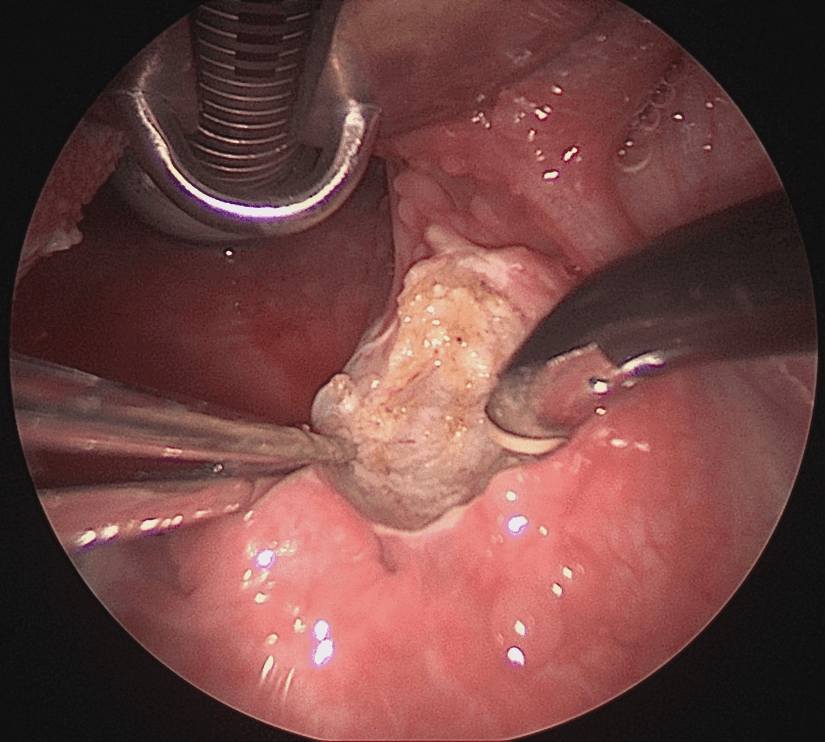

Snoring, OSA & Adenotonsillectomy
Adenotonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of both the adenoids (located at the back of the nasal cavity) and the tonsils (located at the back of the throat). It is commonly performed to alleviate various conditions affecting these structures, particularly in children experiencing sleep-related issues. A child affected with snoring or obstructive sleep apnoea needs to be evaluated first, to assess if their tonsils and adenoids are involved. A video of your child’s sleep may be brought in, to evaluate sleep quality, which will be helpful for the assessment.
They may exhibit signs such as frequent pauses in breathing during sleep and snoring every night. This is considered abnormal in children and warrants consideration for an adenotonsillectomy. Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea are more serious, and it is strongly advised that children with these symptoms undergo the surgical treatment to improve their sleep and overall health.
The surgery is performed under general anaesthesia, ensuring the patient is unconscious and pain-free. Various techniques may be used, including cold knife dissection, electrocautery, coblation, or laser, with COBLATION adenotonsillectomy being the preferred choice from the perspective of optimally effective treatment. Typically, the procedure lasts about 30 minutes to an hour; however, this can vary.
Coblation Adenotonsillectomy combines the use of COBLATION Technology (clicking this opens on separate tab: https://mytonsils.com/) for both adenoidectomy (removal of adenoids) and tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils) in a single surgical session using the precise and controlled radiofrequency energy of Coblation. Application of Coblation Technology can also be seen in other treatments for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) like Palatial Stiffening (CAUP), Tongue Base Channelling & Reduction, and ARIS Coblation Turbinoplasty.
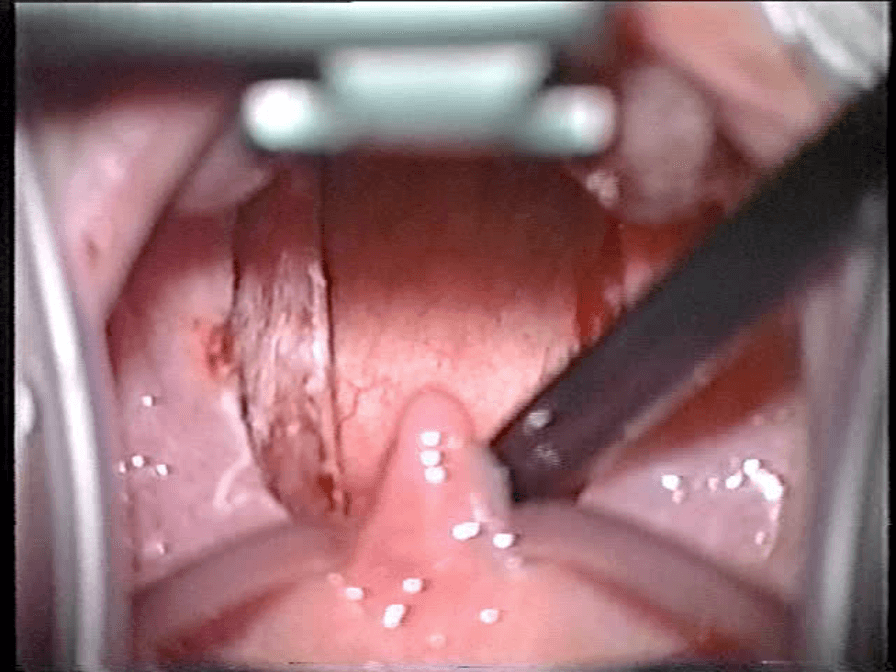
After Surgery
Patients are monitored closely after surgery to manage pain and ensure proper hydration and nutrition. Most children recover fully within 1 to 2 weeks, during which time they may experience throat pain, ear discomfort, and temporary changes in eating and sleeping patterns. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing and address any complications or concerns.